Child Welfare Funding
NRC4Tribes Needs Assessment Findings
Tribal Child Welfare Funding was one of the five overarching themes or topic areas identified through the NRC4Tribes Needs Assessment Findings - Executive Summary and complete NRC4Tribes Needs Assessment Findings. The NRC4Tribes Needs Assessment includes a series of specific findings and recommendations concerning Child Welfare Funding.
Funding for tribal child welfare programs comes from a variety of federal, state and local sources, including funding administered by BIA through the Indian Child Welfare Act of 1978 and its Services to Children and Elderly Families, funding through grants to tribal courts, and funding administered by Health and Human Services (HHS) through Title IV-B (Subpart 1, Child Welfare Services and Subpart 2, Promoting Safe and Stable Families) and Title IV-E Foster Care.
Other Tribal Funding Studies
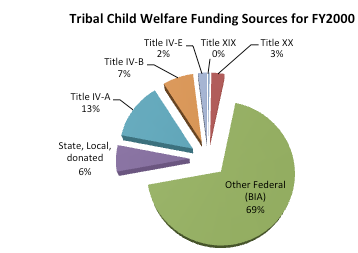
A 2004 study of selected tribal child welfare programs (from “Analysis of Funding Resources and Strategies among American Indian Tribes: Findings from the Study of Implementation of the Promoting Safe and Stable Families (PSSF) Program by American Indian Tribes,” by James Bell Associates, March 31, 2004, p. 5. PDF of report) found that the majority of funding for fiscal year 2000 came from BIA-administered funding (just under 70%) while HHS-administered funding only accounted for 25%, with 2% from Title IV-E and 7% from Title IV-B.
Although HHS funding through Title IV-B and Title IV-E is a relatively small source of funding for tribal child welfare programs, it is an important resource for tribes because it supports the operation of Title IV-E foster care programs, reimburses tribes for eligible services, and provides Title IV-E–eligible training for caseworkers and foster parents. Prior to 2008, Title IV-E funding was available directly to states but was available only indirectly to tribes through tribal/state agreements. As of 2008, there were approximately 90 tribes with tribal/state agreements, and 70 of these allowed for either maintenance, administrative, or training activities funded by Title IV-E.
The Fostering Connections to Success and Increasing Adoptions Act of 2008 (Public Law 110-351) now allows for direct Title IV-E funding to eligibletribes for foster care, adoption assistance, guardianship placements, and independent living services. Currently, tribes may apply for a one-time grant to assist in the development of a tribal IV-E plan.
Fostering Connections Act Addresses Tribal Access to Title IV-E
The chart below shows the complete funding distribution from this study. Although this study focused on a relatively small sample, anecdotal evidence from field practitioners supports the conclusion that the BIA provides the majority of funding for tribal child welfare programs, with some indications of a growth in funding through tribally generated revenue.
|
|
Tribal Title IV-B Funding |
 |
NRC4Tribes Technical Assistance Needs Assessment: Tribal Child Welfare Funding |
|
|
Tribal Title IV-E Funding |
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) concerning Tribal Child Welfare Funding |
|
|
Tribal Court Improvement Program |
|
Fostering Connections website resources concerning Tribal Child Welfare Funding |
|
|
Other Children's Bureau Funding |
|
Bureau of Indian Affairs resources concerning Tribal Child Welfare Funding |
|
|
Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) Funding |
|
General Funding Resources |
